What is democracy?
Democracy literally means that the people (demos) decide (kratos). It is a form of governance where a country’s citizens decide who will lead their country, and how it should be led. As opposed to other forms of governance where the country is led by one or a few people, a democracy is based on the decisions of the majority.
Across the world, many countries claim to be democratic. However, what characterizes a completely developed democracy is the country holding free elections, citizens enjoying the freedom of speech, an independent court and individual human rights.

The principle of separation of powers
The principle of separation of powers requires that principal institutions of state should be clearly divided. This principle stems from the French philosopher Montesquieu. He believed that “those who have power are inclined to abuse it”. To avoid any abuse of power, Montesquieu devised a model in which state power is divided into three independent parts: a legislative, an executive, and a judicial power. This model is called “Checks and balances” and ensures a fully-fledged democracy for all of us.
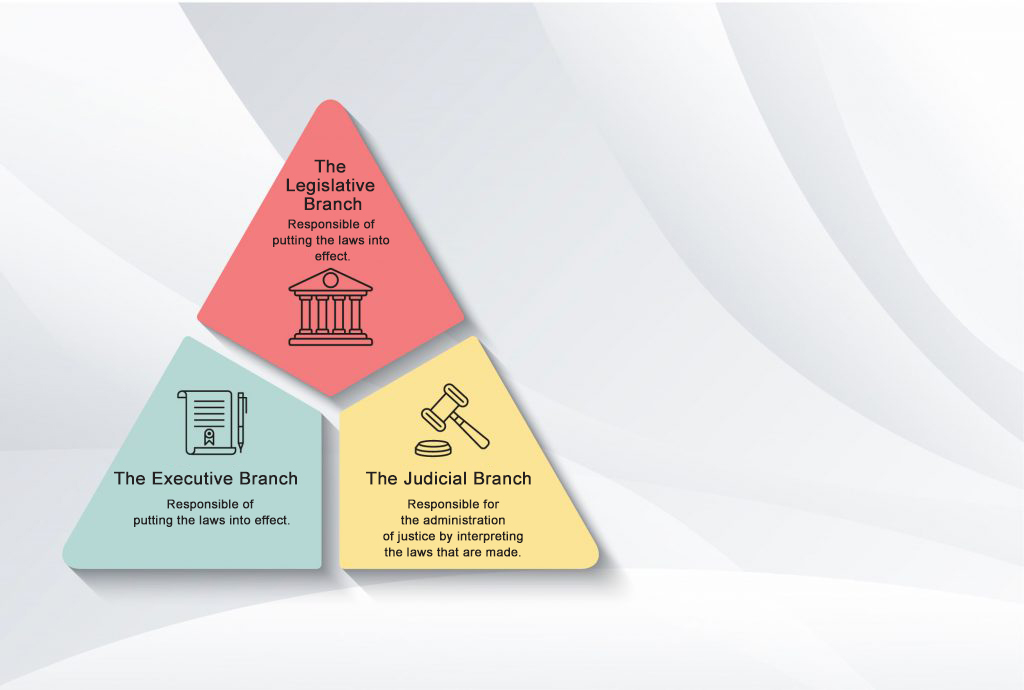
The principle of separation of powers
Ønsker du å lese hele artikkelen?
Ved å logge inn får du full tilgang til artikkelen, samt Lærerrommet med engasjerende læringsstier og oppgaver du kan bruke i undervisningen.
Ønsker du å prøve ut fullversjonen av Skolerom?
Kontakt oss her!
