What is democracy?
The word democracy means that the people (demos) decide (kratos). The people who live in the country decide who will lead the country. This is different from other forms of ruling, where one or a few people lead the country.
Many countries say that they are democratic, but that is not always true. To be a democratic country, you need to have free elections, freedom of speech, an independent court and individual human rights.

The principle of separation of powers
The principle of separation of powers is about how power is divided. This idea comes from the French philosopher Montesquieu. He thought that those who have power would probably abuse their power. To avoid power abuse, he created a model where the power is split into three parts: legislative, executive, and judicial power.
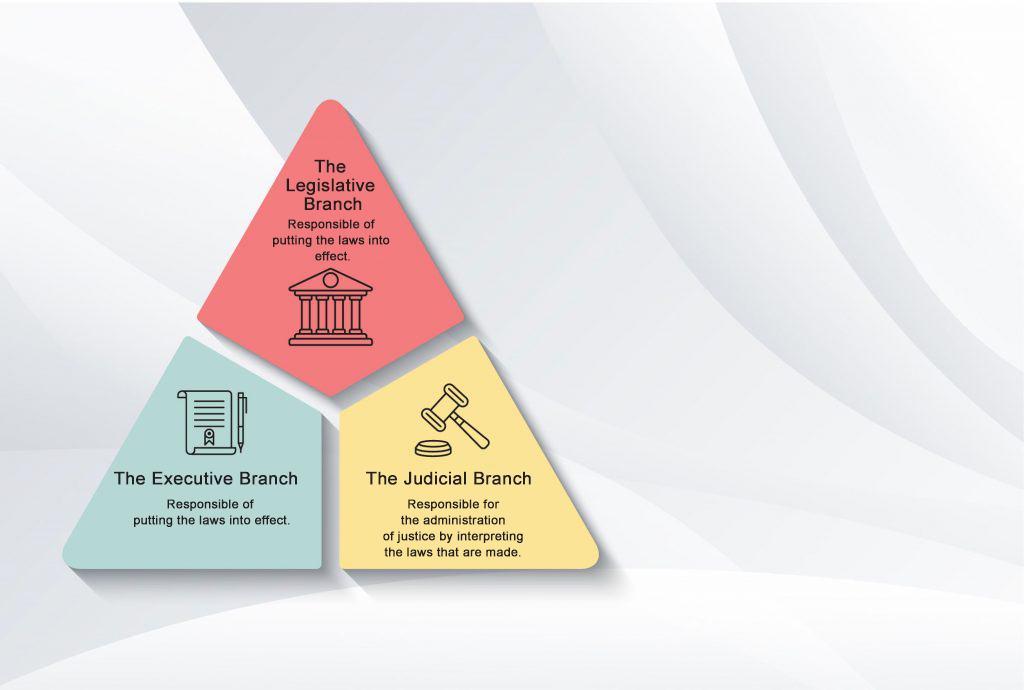
The principle of separation of powers
The democratic system of the UK
The law-making power
Parliament is the law-making power. They can create or end any law, for example the law that every child has the right to education.
Parliament is made up of three parts: the House of Commons, the House of the Lords and the Crown.

Houses of parliament in London, UK
The executive power
The government is the executive power. They are responsible for carrying out laws, but also the running of local and national tasks like rubbish collection and the police.
The executive power is made up of the Crown and the Government, including the Prime Minister and the Cabinet ministers.


UK Supreme Court facade in the City of Westminster
The separation of powers

Interior of the House of Commons before 1834

The Mall in Westminster City London

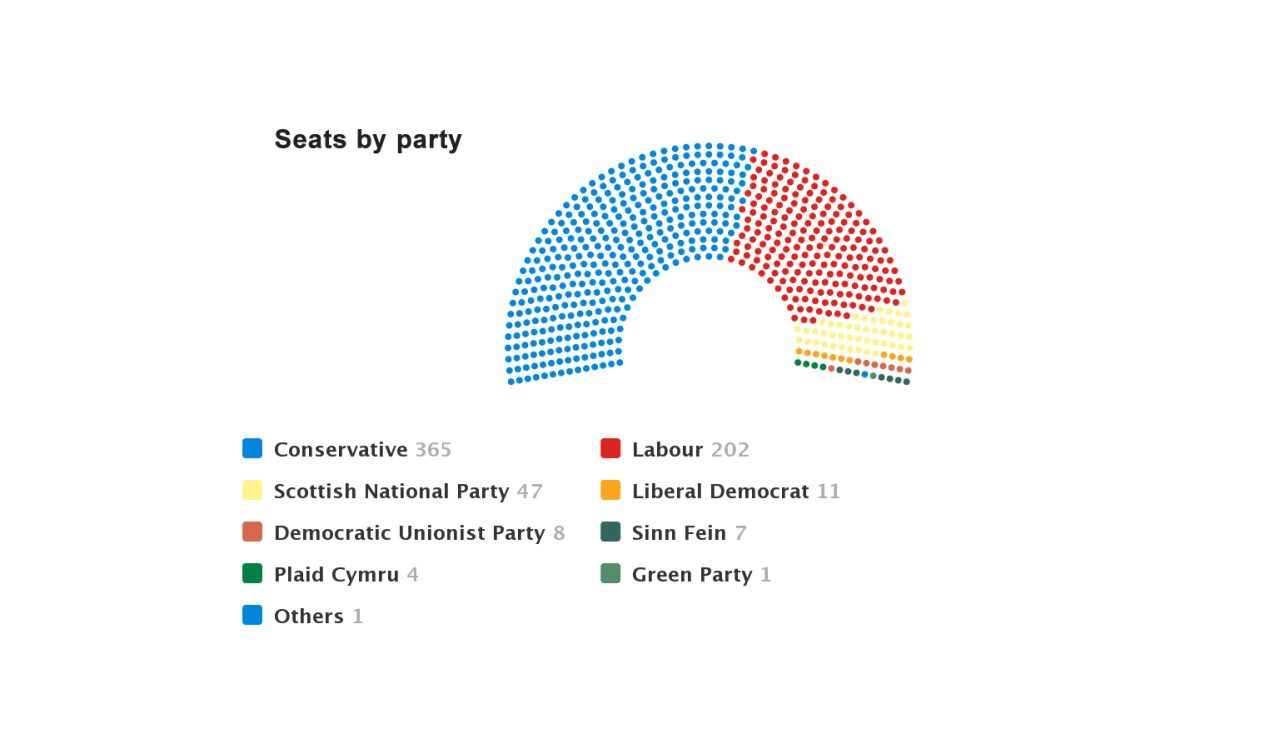
Chart, seats by party, House of Commons
What is the Left Wing and the Right Wing?
Different forms of democratic ruling
The UK is a constitutional democracy. That means that the king doesn’t have any formal power. The power lies with the Parliament, where people have voted for the representatives.
The opposite of a monarchy is a republic. In a republic, you have an elected president who has the power. Finland, France and the US are examples of republics.
The US democratic system
The United States is a republic state. This means that the US doesn’t have a king or queen. There are 50 states that can decide many of their laws on their own. For example, Texas in the South has completely different laws to those of Minnesota in the North. The central power of the US lies in Washington D.C.
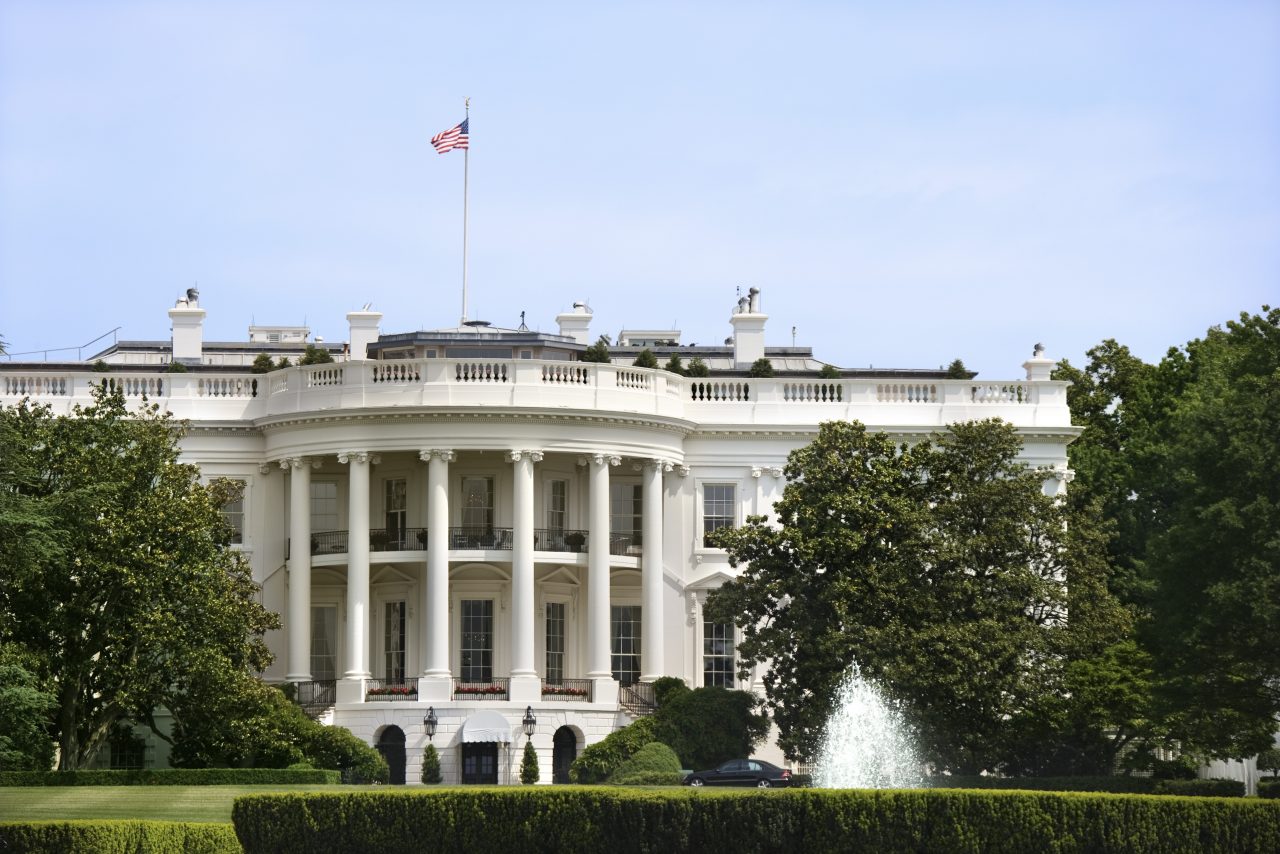
⬅ This is the White House in Washington D.C., the residence of the presidential family.

The distribution of power in the United States
The executive power
In the US, the President is the executive power. The president is elected every four years and can only be re-elected once.
Former presidents Barack Obama and Donald Trump in the Oval Office shortly after Trump won the Presidential election in November 2016.


The United States Capitol building at sunset, Washington DC, USA.
The judicial power
The Supreme Court is the judicial branch of the United States of America, and it makes sure that the US Constitution is followed across the country.
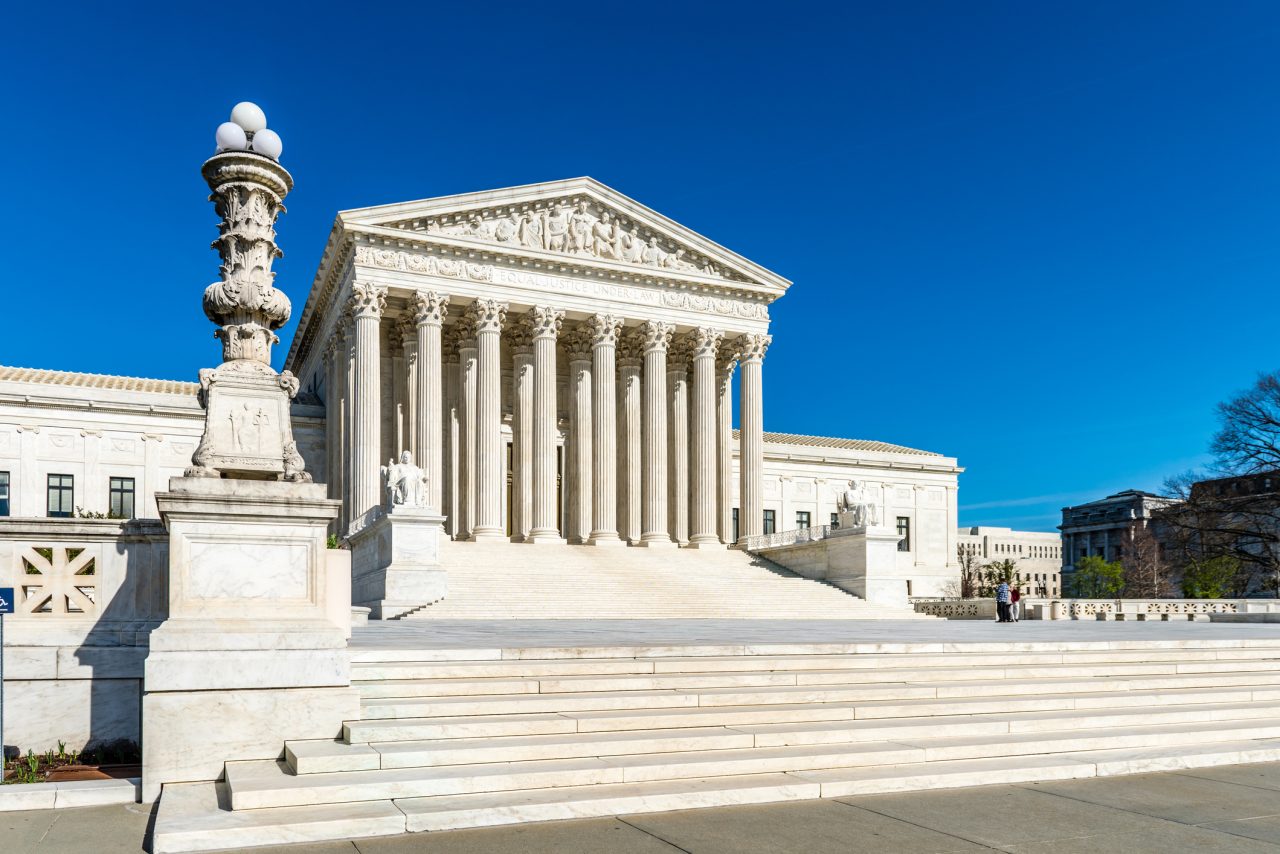

The United States Supreme Court Building in Washington D.C.

A high angle shot of the inside of the New York Public Library, USA

United States Court House in the Civic Center district of New York City.
Local governments
Local governments get power from the state to take responsibility for example for parks, police services and transportation in towns.

A lot of police cars stuck in traffic in New York.



