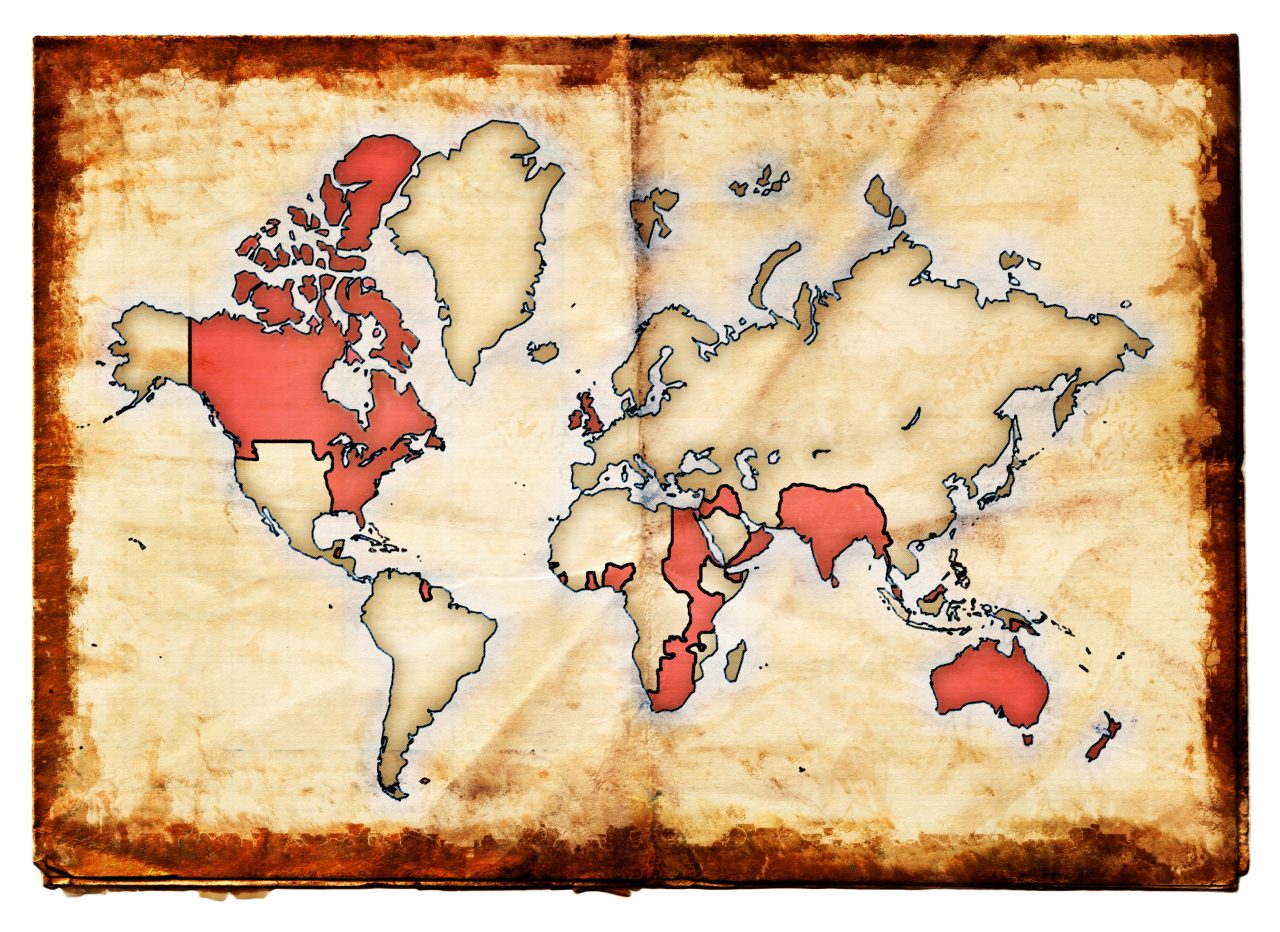
English is the third most spoken first language in the world, but is also used by many as a second language. But how has English become so widespread that we can call it a world language?

The spread of English
English is spoken all around the world. In countries like the UK, Ireland, the US, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, India and South Africa, English is an official language. Also, many of the islands in the Caribbean and the Pacific use English.
There are actually as many as 402 million people who speak English as their first language, while there are between 350 million and a billion who use English as a second language – as we do in Norway.
What other languages do you think are considered world languages?
Lingua franca
Lingua franca is a general term for communication between people who do not have the same mother tongue, and therefore use a different third language to communicate.
Imagine that you are a native speaker of Norwegian and have to talk to someone whose native language is German. If neither of you speak the other language, what do you do? Well, you can use a language that you can both understand when you talk to each other. In many cases, this will probably mean that you will use English, since many children start learning this language as early as in first grade.

Mennesker på en åpen plass hvor alle er koblet sammen i hverandre.

Illustrasjon av vikingskip ute på havet

Bayeux-teppet eller dronning Mathildes tapet er et 70 meter langt og 0,5 meter bredt brodert veggteppe i lin fra omkring år 1070. Det fremstiller normannerhertugen Vilhelm Erobrerens invasjon av England og slaget ved Hastings i 1066.
Papir bakgrunn med William Shakespeares signatur
How far back in time could you go and still understand English?

Papirbakgrunn
Global English

Papirbakgrunn
When do you use English?
In Norway, most children and young people use English when they watch YouTube, play games and watch films or series, while they use Norwegian when they read the news.
When do you use English in your everyday life?

En mobil med svart skjerm. Ikoner rundt en tekst der det står 'English'. Ikonene skal illustrere hvor man kan lære og bruke engelsk.
Sources:
- ICAL TEFL (03.01.2023): Old English vs Modern English
https://icaltefl.com/old-english-vs-modern-english/
- Politicworm (12.12.2022): How he spelled his name
https://politicworm.com/oxford-shakespeare/to-be-or-not-to-be-shakespeare/why-not-william/the-authorship-question-2/how-he-spelled-his-name/
- Wikipedia (19.12.2022): Great Vowel Shift
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Vowel_Shift
- OpenLearn (03.01.2023): From Old English to Modern English
https://www.open.edu/openlearn/history-the-arts/english-language/from-old-english-modern-english
- The education daily (03.01.2023): Why English became The Global Language
https://theeducationdaily.com/2021/08/why-english-became-global-language
Media Rights:
-
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images / Yifan Chen – YouTube
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images / Yestervid– YouTube
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images / OpenLearn from The Open University – YouTube
-
Getty Images
-