Fake news
“Fake news” can seem like harmless lies. However, the worst case scenario is that fake news can be a threat to democracy and contribute to the formation of violent movements.


What is fake news?
Fake news is false information. It can be lies or untruths, often created by unreliable websites, and shared through online posts, comments and images in news and social media.

Fake News-logo
Why do people create fake news?
Two reasons are:
- Political interest, hoping to influence opinions and attitudes in society.
- Make money.

Mørk bakgrunn
Example 1:
Anti-vaccinationists
Anti-vaccinationists are also called anti-vaxxers. Some anti-vaxxers believe vaccinating children can cause autism. There is no proof to support this, but wrong information is spread in social media and many people believe it. The World Health Organization considers the fight against vaccines to be one of the world’s biggest health threats.
Vaksine
Example 2:
“The China Virus”
Donald Trump, and many others, have said that COVID-19 was created by the Chinese to damage the USA. This spread fast among Trump supporters in social media. The opposite happened in China. Some people claimed that the virus was planted in Wuhan by American soldiers to damage China.

Donald Trump på talerstolen
Political movements
Fake news often comes from undocumented claims. The goal is to get more power or change policies. Such claims can end up challenging democracy and adding to raise violence.

Knyttede never
Example 3:
The Holocaust
During World War II the German Nazis blamed the Jews for Germany’s problems in the 1930s. The spread of misinformation about the Jews lead up to what is today called the Holocaust; the massacre of more than 6 million Jews.


Mørk bakgrunn
Example 4:
QAnon
QAnon is an American group working to make Donald Trump more popular. They have a conspiracy theory that the world is ruled by democratic politicians and others, in a powerful and Satan-worshiping elite. QAnon supporters have been known to become violent, and were involved in the attack on the US Capitol in Washington, D.C. on January 6, 2021.
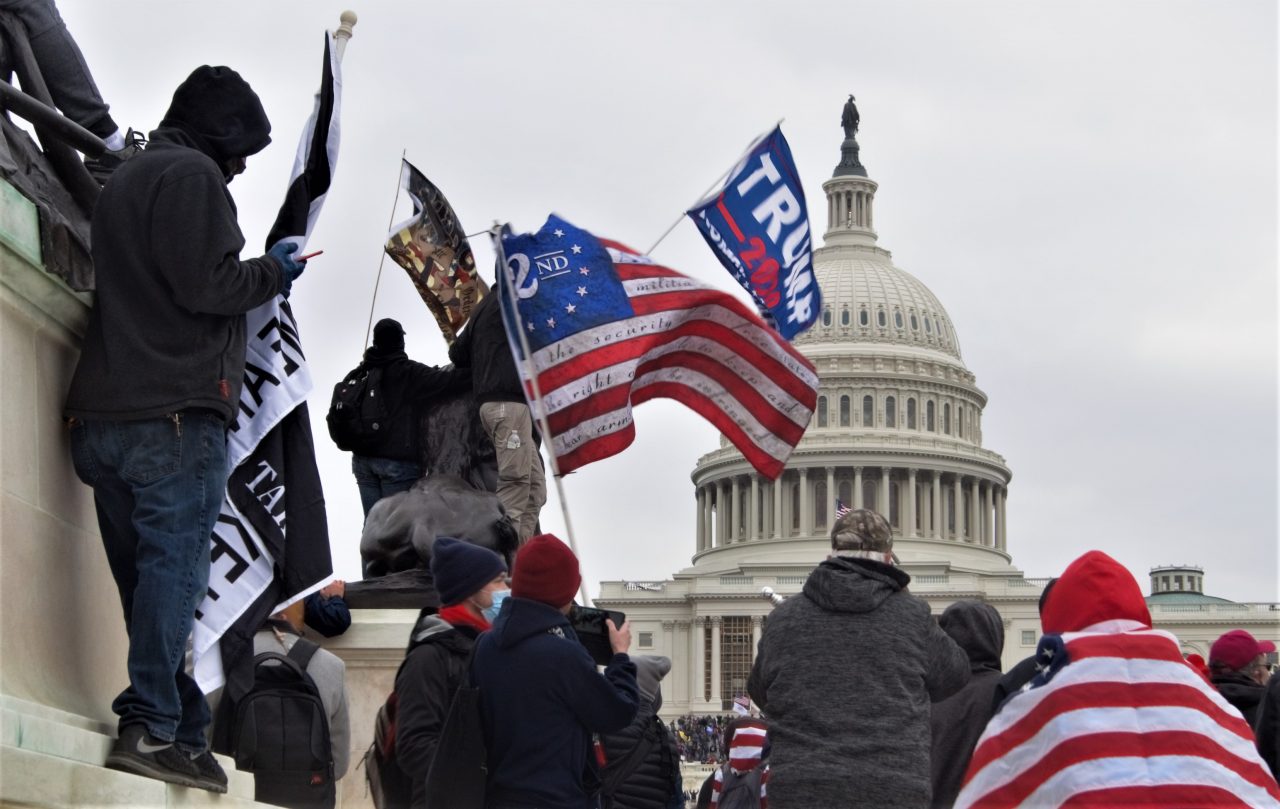

Stormingen av kongressen i USA
Fake news spreads fast
Fake news spreads fast. Fake news can be shared on the internet and in social media by anyone. Many people can be exposed to the news very fast. It can be difficult for the reader to know what is fake and what is real news. If someone believes the fake news, they may spread it on their own social media.

Forstørrelsesglass
Sources:
- Medietilsynet (09.01.2021): Slik avslører du desinformasjon og falske nyheter https://www.medietilsynet.no/mediebildet/slik-avslorer-du-falske-nyheter/
- Kildekompasset (09.01.2021): Hva er kildekritikk?
https://kildekompasset.no/kildekritikk/
- Orgeret, Kristin Skare: kildekritikk i Store norske leksikon på snl.no.
Hentet 5. mars 2021 fra https://snl.no/kildekritikk
- Banik, Vibeke Kieding: Holocaust i Store norske leksikon på snl.no.
Hentet 5. mars 2021 fra https://snl.no/Holocaust - Cambridge Dictionary (hentedato: 20.06.2022)
https://dictionary.cambridge.org/
Media Rights:
-
-
Getty Images
-
Faktisk – YouTube
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Gage Skidmore (CC BY-SA 2.0)
-
Getty Images
-
Bundesarchiv (CC BY-SA 3.0)
-
Tyler Merbler (CC BY 2.0)
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-
Getty Images
-


